





Release time:2024-08-15 Browsed1 order
There is a detail that users may have noticed: the transmission distance of the IoT wireless module is often a range, rather than an accurate value.
Why is this?
In fact, the reason is very simple. The transmission distance of the wireless module is often affected by various factors. The transmission distance
will be different in different environments, weather, and stages.
If a wireless module can transmit 5km under normal conditions, when it is deployed in an environment with frequent interference or bad weather,
the transmission distance may not reach 5km.
So, how can we make the wireless module suitable for a variety of environments and ensure that data is transmitted to our target device safely and
stably? What is co-channel interference?
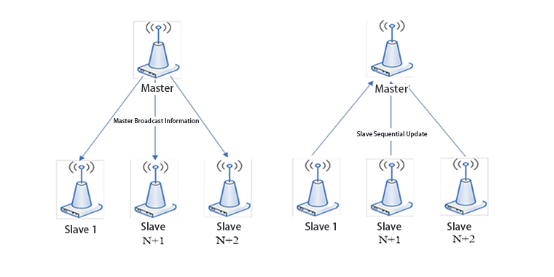
1. Master Polling Mode
The master polling method is a method in which the master polls and calls out numbers one by one. The principle is very simple, and the response is
achieved by calling the roll. For example, the master sends a message to slave No. 1. Since the slaves have addresses, only slave 1 can respond to the
master. After receiving the command from the master, slave 1 uploads the data to the master . The master then polls the data of other slaves in the
same polling method.
To use an appropriate metaphor, when the teacher (master) is in class, he calls student No. 1 (slave) to answer questions. At this time, only student
No. 1 can answer the teacher's questions. This is the master polling method. The advantage of the polling method is that it is not easy for conflicts
to occur between devices, and the networking is relatively stable, but the disadvantage is that the master polling takes a long time. This networking
method is suitable for networking applications that do not require high time.

2. Slave Timing Upload Mode
The principle of the timed upload method is that the master broadcasts information to the slave. After receiving the master information, the slave
synchronizes the time and then uploads according to the time we set. For example, after the master sends information, the upload time of
slave 1 is 1 second, then the upload time of slave 2 is 2 seconds... and so on. For example, during our military training, the instructor issued an order
to us and required us to report numbers from left to right. The first person on the left reported the number 1, the second person reported the number 2,
and so on. The principle of timed upload is the same. Set the upload time of the slave to avoid uploading data at the same time, so as to avoid the same frequency interference.
3. Active Upload Mode From Slave
The slave actively uploads, and the networking mode of the LoRa module with its own RSSI function is a relatively reliable active upload method.
This transmission method is to detect the RSSI signal strength in the environment when the slave needs to upload data. If the RSSI strength in the
current environment is large, it will wait for the RSSI value to become smaller before actively uploading. Whether the upload is successful, the master
will feedback to the slave to decide whether it needs to be re-uploaded. However, this method is not suitable for LoRa modules without RSSI function,
because the more frequently the slave uploads, the higher the probability of communication failure, which is what we call co-frequency interference.